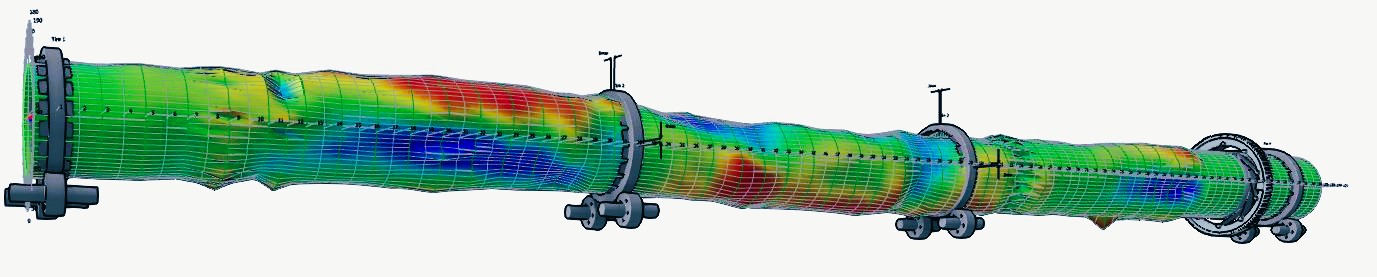
Kiln Crank (Roller Shaft Deflection)
Crank in a kiln—whether mechanical or thermal—is a critical alignment issue that is difficult to detect during normal operation but can be identified through proper measurement. Even small deviations can disrupt the straightness of the kiln axis, causing abnormal stresses on the shell, tyres, rollers, and bearings. This leads to accelerated wear, higher maintenance costs, and unplanned downtime. Early detection and corrective action are essential to maintain stable operation, extend equipment life, and avoid costly interruptions.
Mechanical crank: A permanent deformation that requires repair. It is typically caused by shell deformation or incorrectly aligned shell sections during replacement and welding.
Thermal crank: A temporary deformation usually resulting from uneven heating of the kiln shell. Common causes include coating build-up, refractory failure, sudden kiln stoppages without proper cooling, or localized hot spots.